The Cane Corso is a grand dog. It is very loyal. People respect it. Owners need to know about their health. These dogs live 9 to 12 years. This guide looks at Cane Corso health. It uses "Good, Bad, and Ugly." It talks about their strengths. It also covers their weaknesses. This helps owners care for their dog. Good owners keep their dog healthy.
Key Takeaways
Cane Corsos are strong dogs. But they can get certain health problems. These include hip issues, bloat, and heart disease.
Good breeders check their dogs. They do this before breeding them. This helps make sure puppies are healthy.
Feed your Cane Corso small meals often. Avoid exercise around meal times. This can help stop a dangerous problem. It is called bloat.
Take your Cane Corso to the vet often. Give them healthy food. Make sure they get enough exercise. These things keep your dog healthy and happy.
Look for signs of sickness. Get help early. This can really help your Cane Corso's health.
The Good: Cane Corso Health Strengths

Cane Corsos have many good health traits. These traits help them stay healthy. Owners often see these dogs as strong. They have many good points.
Overall Hardiness and Resilience
The Cane Corso is a tough breed. They are very resilient. This strength helps them live long lives. Scientists study their genes. They look for markers linked to long life. For example, the TDRP gene is key. It helps with sperm health. Its 3'UTR part may control genes. These genes are important for a long life. The MC2R gene affects hormones. Changes in this gene can cause problems. These problems can shorten a dog's life. FBXO25 helps tumors grow. It is near TDRP. This area is important for long life. FBXL21 has a special marker. This marker changes an amino acid. It is in dogs that live long. It is vital for body clocks. These clocks affect aging.
| Genetic Marker | Contribution to Hardiness (Longevity) |
|---|---|
| TDRP | Associated with spermatogenesis and sperm motility; its 3'UTR region may regulate gene expression crucial for longevity. |
| MC2R | Involved in adrenocorticotropic hormone regulation; variations can lead to conditions like hyperadrenocorticism and adrenocortical tumors, which shorten lifespan. |
| FBXO25 | Plays a role in promoting tumor growth; its close proximity to TDRP suggests this chromosomal region is significant for longevity. |
| FBXL21 | Contains a longevity-associated SNP in its exon, leading to an amino acid change (tryptophan instead of arginine) in long-lived dogs; crucial for circadian rhythms, which influence aging. |
Strong Immune Systems
Cane Corsos often have strong immune systems. They fight off common sicknesses well. This means fewer vet visits. They avoid small infections. A healthy immune system is good. It helps the Cane Corso stay active. They also stay lively.
High Pain Tolerance and Physical Strength
The Cane Corso is a strong dog. They can handle a lot of pain. This comes from their past. They were working dogs. A Cane Corso can handle discomfort. Their physical strength is great. They can do many hard tasks. The strong body of the Cane Corso makes them tough.
Fewer Common Ailments Compared to Some Breeds
Many breeds get sick often. The Cane Corso has fewer such issues. This is a health benefit. Owners like their Cane Corso's strong health. This good health helps the dog live happily. The Cane Corso often avoids problems. Other large breeds often have these problems.
The Bad: Common Cane Corso Health Concerns
Even strong breeds have problems. The Cane Corso has specific health concerns. Owners must know about these. They are common health issues. Knowing helps them give the best care. This part talks about big cons. These are for the Cane Corso breed.
Hip and Elbow Dysplasia Risks
Hip and elbow dysplasia are common. They are skeletal issues. They affect large dog breeds. Joints do not grow right. This causes pain. It leads to arthritis. Dogs can become lame. The Cane Corso often gets hip dysplasia. Vets check many dogs.
| Breed | Evaluations | Percent Dysplastic |
|---|---|---|
| Cane Corso | 876 | 39.0 |
This table shows 39% of Cane Corsos. They have hip dysplasia. This is a big health problem. Elbow dysplasia also affects them. Good breeders check their dogs. They use X-rays. This checks joint health. Finding it early helps. It helps manage symptoms.
Bloat (GDV) Prevention and Care
Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus is bloat. It is very dangerous. The stomach fills with gas. Then it twists. Blood flow stops. Vets must act fast. Some things raise the risk.
- Getting older
- Having a family member with GDV
- Eating from a raised bowl
- Eating dry food with fat. It is in the first four ingredients.
- Eating dry food with citric acid
- Wetting dry food with citric acid. This is before feeding.
The Cane Corso can get this. Other breeds also get it a lot.
| Breed | GDV Prevalence GDV |
|---|---|
| Great Danes | 14.0% |
| Akitas | 9.2% |
| Dogue de Bordeaux | 7.2% |
| Irish Setters | 7.1% |
| Weimaraners | 7.1% |
Owners must prevent it. This is key for Cane Corso owners.
- Feed small meals. Do this several times a day. Do not feed one or two big ones.
- Do not exercise right before eating. Do not exercise right after.
- Stop your dog from drinking too much water. Do not let them drink fast.This is true during meals.
- Help them eat slowly. Do this in a calm place. This stops them from gulping air.
- Use a slow feeder bowl. Or spread food on a sheet. This is for fast eaters.
- Do not use raised food bowls. They cause more GDV.
- Pick good dog food. It should be low in carbs. It should be high in protein.
- Wet dry food. This helps it digest easier.
- Avoid brewer's yeast. Avoid soy products.
- Choose food with meat meal. It should be in the first four ingredients.
- Reduce stress. Especially at meal times. Feed calm dogs. Feed them in separate rooms. This is for homes with many dogs.
- Talk to your vet about gastropexy. This is if your dog is at high risk.
"I have a 1 year old Cane Corso. I had never heard of Bloat or anything like that before but when I started to read and hear more about it I decided I needed my baby to be protected. I scheduled her for her Spay and Gastropexy at the same time. as recommended, unfortunately due to some equipment malfunction they were unable to do the Gastropexy and want to reschedule 2 weeks after she has been spayed. My concern is with the 2 surgeries being so close together and her recovery in between. Do you think it would be better to wait?"
Gastropexy is a surgery. It prevents problems. A vet stitches the stomach. It goes to the belly wall. This stops it from twisting. It does not mean bloat will not happen. But it stops full twisting. This lets fluids and gas pass. It gives more time for vet help. This surgery can be done with a scope. This makes it less invasive. It can also be done with a spay or neuter. This lessens surgery effects.
Eyelid Abnormalities: Entropion and Ectropion
Cane Corsos can have bad eyelids. Entropion makes the lid roll in. Eyelashes rub the eye. Ectropion makes the lid roll out. This shows the eye. Both cause pain. They can cause infection. They can cause vision problems. Another common illness is 'cherry eye.' The third eyelid gland pops out. Vets use methods to fix it. They use tacking and pocket methods. These usually work well. Success rates are 75% to 100%. Some dogs need a second surgery. This depends on the breed. It depends on how bad it is. It depends on the surgery type. Removing the gland is a last choice. It can cause dry eye. This happens in 40% of dogs.
A changed pocket method works well. It holds the gland in place. One study looked at 126 eyes. It showed 99.2% success. This was after one surgery. It rarely came back. Only 0.8% of cases. Some problems happened right after. These included cysts (4%). Also, eye sores (1.6%). But the method worked very well long-term.
Cardiac Health Issues: DCM
Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a heart problem. It affects the Cane Corso. DCM makes the heart muscle thin. It makes it weak. The heart cannot pump blood well. Dogs with DCM may seem tired. They may cough. They may have trouble breathing. This can lead to heart failure. Regular vet visits help find DCM early. Early finding helps manage it. This is done with medicine.
Joint and Ligament Injuries
Big, active dogs get injuries. The Cane Corso gets joint and ligament injuries. Cruciate ligament tears are common. These often need surgery. Long-term care is important. It helps recovery. It stops future issues.
- Weight management: Being too heavy makes risk four times higher. Losing weight is key. It can reduce surgery needs. It also slows arthritis. Keeping a pet thin helps joints. It lowers swelling.
- Exercise modification: Regular, controlled activity is good. This includes stretching. It includes moving joints. It includes controlled walking. Swimming helps too. Special exercises from therapists help. These include balance boards. Underwater treadmills help. This keeps joints moving. It builds muscle. It keeps them comfy.
- Joint supplements/adjunctive therapies.
- Pain management: This means using anti-inflammatories. Or pain medicines.
Long-term care for injuries involves:
- Pain relief. This is ongoing. It uses drugs and supplements.
- Exercises for recovery.
- Managing weight.
- Glucosamine Supplements For Dogs and fatty acids. These protect joint cartilage.
- Dog-specific anti-inflammatory drugs. Examples are carprofen (Rimadyl). Also meloxicam (Metacam).
- Human pain meds like tramadol (Ultram). These are extra.
- Many rehab treatments. These include physical therapy. Also hydrotherapy. They are vital for recovery. They are vital for long-term joint health. This is true for weight loss. It is true for muscle building.
Owner help is key. It helps long-term success. It stops problems. Key home care includes:
- Strict exercise control: Limit activity. Only short walks on a leash. Do this until the vet says it's okay.
- Incision monitoring: Check daily for infection signs.
- Keeping incisions dry: Do not bathe or swim. Do this until it heals.
- Medication compliance: Give all prescribed meds. Give pain meds. Give anti-inflammatories. Do this on time.
- Follow-up visits: Go to all check-ups. This is for assessment. It is for rehab advice.
The Ugly: Serious Cane Corso Health Conditions
Serious health problems can strike the great Cane Corso. Owners must know about these challenges. Finding them early is key. Smart choices help manage these big issues.
Cancer: Lymphoma, Osteosarcoma, Mast Cell Tumors
Cancer is a big danger. It affects many large breeds. This includes the Cane Corso. Owners often make hard choices. This is when their dog gets cancer. Lymphoma, osteosarcoma, and mast cell tumors are common. They affect this breed. Osteosarcoma is bone cancer. It grows fast. It often hits big dogs. Helen was a Cane Corso. She was 8.5 years old. She joined a study for osteosarcoma. This study used amputation. It also used histotripsy. This uses sound waves. It breaks down sick tissue. Helen's fight helps new cures.
How long dogs live with cancer varies. It can be 2 to 15 months. This is with treatment. Each dog's outcome is not known. Strong treatments for bad cancers. They often have higher risks. These are for serious problems. Many things affect treatment choices. These include the pet's nature. Also, their mood. And if they can travel. Family life matters. The dog's age matters. Other problems matter too. Like heart failure. Or kidney problems. These can limit treatment.
A good life is most important. A few months of pain. This might be worth years of good life. But it is not worth it. Not for only a month or two.
Dr. Sue Ettinger is a vet cancer doctor. She says treat the pet. If it will live longer with treatment.
If strong treatment is not chosen. Or if it's not right. Other care can help. This is called palliative care. It gives comfort. It includes pain pills. Also, prednisolone. And general comfort care. Palliative care eases pain. It helps with swelling. It helps with sickness. It keeps the dog comfy. It helps them enjoy their last time.
Epilepsy: Genetic Predisposition and Management
Epilepsy is another big worry. It affects the Cane Corso. Idiopathic epilepsy is a big problem. It runs in Cane Corsos. This condition is genetic. It is like hip dysplasia. It is passed down. Sick dogs should not breed. This stops it from spreading. The exact cause is unknown. But breeders know about it. It usually starts. This is between ages 1 and 5. It causes seizures. There is no known reason. Medicine often helps manage it. It controls seizures. Regular vet checks are vital.
Demodectic Mange: Immune-Related Skin Condition
Demodectic mange is a skin problem. It is linked to the immune system. It affects the Cane Corso. This mange happens. It is from too many Demodex mites. These mites live on dog skin. A weak immune system. It lets them grow too much. This makes skin itchy. Hair falls out. Other infections start. Treatment often uses special shampoos. Also, dips. Or pills. It also fixes immune system problems.
Thyroid Issues: Hypothyroidism
Thyroid issues also affect the Cane Corso. Hypothyroidism is a common problem. It is an endocrine disorder. It happens when the thyroid gland. It does not make enough hormones. The Cane Corso gets hypothyroidism more often.
| Source | Incidence |
|---|---|
| OFA 2023 testing | Over 7% |
| Condition | Incidence |
|---|---|
| Hypothyroidism | 5-10% |
Symptoms include weight gain. Also, being tired. Hair loss. And skin problems. Vets find hypothyroidism. They use blood tests. Treatment means daily medicine. It replaces thyroid hormone. This medicine helps manage it well.
Proactive Cane Corso Health Management
Good ownership helps a Cane Corso. It lives a long, healthy life. Owners can do many things. These manage their Cane Corso's health. They make sure the dog gets the best care. Taking early steps is very important.
Choosing a Reputable Breeder: Health Clearances
Picking a good breeder is the first step. Good breeders give health papers. These papers cover the puppy. They also cover its parents. They focus on common problems. These include hip dysplasia. Also, eye problems. And some heart conditions. Good breeders try to lower these risks. They pick breeding dogs carefully. They also give regular veterinary care. Breeders are open about what they do. They share genetic test results.
Look for specific papers from breeders:
- OFA papers for hip dysplasia
- PennHIP papers for hip dysplasia
These papers show they care about health. They include:
- Hip checks (excellent, good, or fair). These are from the Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (OFA).
- Hip scores from the University of Pennsylvania (PennHIP).
- Eye papers from the Canine Eye Registry Foundation.
Nutrition and Diet for Optimal Health
Good food is key for a Cane Corso. It helps them grow. It helps their overall well-being. The right food changes with age.
| Age Group | Meal Frequency | Daily Food Amount (cups) |
|---|---|---|
| Puppies (2-6 months) | 3-4 times a day |
3-4 cups |
| Adolescents (6 months-1 year) |
2-3 times a day |
4-6 cups |
| Adults (1 year and above) |
2 meals a day |
4-6 cups |
| Seniors (8 years and above) |
Varies | 3-5 cups |
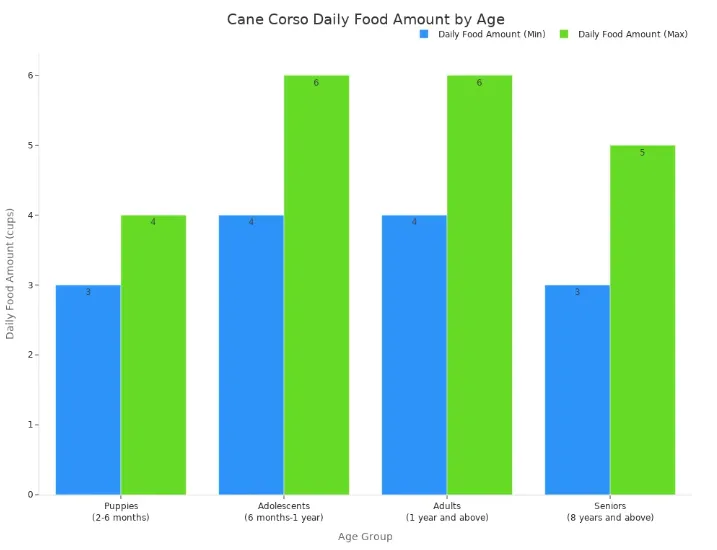
A bar chart showing the minimum and maximum daily food amounts in cups for Cane Corso puppies, adolescents, adults, and seniors.
A balanced diet has certain nutrients:
- Protein: Aim for 25-30%. This is for muscle growth. It is for overall health.
- Fats: Moderate content of 10-15%. This is for essential fatty acids. It is for skin and coat health.
- Carbohydrates: Use whole grains or vegetables. These give energy.
- Joint Health: Include Best Glucosamine For Dogs and Dog Hip And Joint Supplement. These help joint health. They help movement. This is extra important. Hip dysplasia is common.
- Eye Health: Include omega-3 (DHA and EPA). These are from algal or fish oils. They help eye health. Cherry eye is common in this breed.
Exercise and Weight Management
Regular exercise keeps a Cane Corso fit. It also helps control their weight. This stops many health problems. An adult Cane Corso needs steady activity.
- Daily Outings: An adult Cane Corso needs a morning walk. It should be at least one mile. They also need a similar evening walk.
- Activity Type: These walks mean fast walking. Or jogging. Or biking next to the dog.
- Dedicated 'Work' Time: Besides walks, spend 20 minutes daily. Do 'work' activities. These include training. Also, fetching. Or playing. This helps their body and mind.
Good weight control lessens joint stress. It also lowers the risk. This is for other health issues.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups and Preventative Care
Routine veterinary care is very important. For a healthy adult Cane Corso, an annual check-up is advised. This is with a veterinary professional. But how often they visit the vet can change. It depends on the dog's needs. These visits include vaccinations. They also include health screenings. These preventative care visits help find problems early. They make sure the cane gets good care.
Early Detection and Intervention
Owners must watch for sickness signs. Finding problems early helps a lot. This is especially true for a cane corso.
- Difficulty Moving or Limping: Watch for limping. Or trouble standing. Or pain when moving. These can mean joint problems. Hip and elbow dysplasia are common. This is in large breeds.
- Bloating or Distended Abdomen: A swollen belly. Restlessness. Pacing. Trying to vomit but nothing comes up. These are signs of Bloat. This is a medical emergency.
- Changes in Eating or Drinking Habits: Drinking and peeing a lot more. This can point to conditions. These include diabetes. Or kidney disease. Not wanting to eat suddenly. This could mean stomach problems. Or more serious health issues.
- Difficulty Breathing: Any clear changes in breathing. This includes short breaths. Wheezing. Or panting too much. These can mean heart disease. Lung problems. Or heat stroke.
- Sudden Aggression or Behavioral Changes: Unexpected anger. More worry. Or hiding. This is in a calm cane corso. It could be a sign of pain. Or brain problems.
Acting early for hip dysplasia helps a lot:
- Early help for young hip dysplasia. This can make the joint stable. This is as the puppy grows.
- If hip dysplasia is found early. This is in dogs under 1 year old. Surgery can be an option.
- The PennHIP test can be done. This is on puppies as young as four months. This helps owners be ready. They know if their pet is at high risk. This is for hip dysplasia.
The Cane Corso has many health traits. Some are strong. Some are challenging. Owners need to know this. Good care is important. It helps them live longer. It makes them healthier. Knowing these things helps owners. They can give the best care. This helps their corso live long. Every cane does well with good owners.
FAQ
What are the most common health problems for a Cane Corso?
Hip and elbow dysplasia are common. Bloat is very serious. Eyelid problems happen. Heart issues like DCM also occur. Owners must watch for these.
How can owners prevent bloat in their Cane Corso?
Give small meals often. Do not exercise before eating. Do not exercise after eating. Use a slow feeder bowl. Do not use raised bowls. Talk to your vet about gastropexy surgery.
What is the best way to manage a Cane's weight?
Regular exercise is key. Daily walks help. Play time helps too. A good diet stops fatness. Healthy weight helps joints.
How often should a Cane Corso visit the vet?
Adult canes need a yearly check-up. Puppies need more visits. Older canes need more visits. Regular checks find problems early. This keeps your cane healthy.









0 Comments